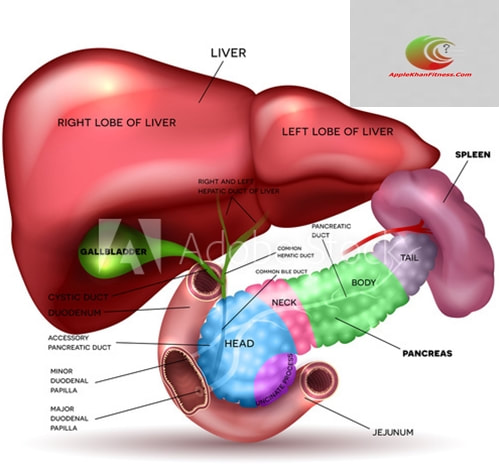
Understanding diabetes and Your Pancreas:
In people with diabetes, the pancreas either produces little or no insulin, or the cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced. A direct connection exists between the pancreas and diabetes. The pancreas is an organ deep in your abdomen behind your stomach. It’s an important part of your digestive system. The pancreas produces enzymes and hormones that help you digest food. One of those hormones, insulin, is necessary to regulate glucose. Glucose refers to sugars in your body. Every cell in your body needs glucose for energy. Think of insulin as a lock to the cell. Insulin must open the cell to allow it to use glucose for energy.
If your pancreas doesn’t make enough insulin or doesn’t make good use of it, glucose builds up in your bloodstream, leaving your cells starved for energy. When glucose builds up in your bloodstream, this is known as hyperglycemia. The symptoms of hyperglycemia include thirst, nausea, and shortness of breath. Low glucose, known as hypoglycemia, also causes many symptoms, including shakiness, dizziness, and loss of consciousness. Hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia can quickly become life-threatening.
What is diabetes?
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that occurs when your blood sugar (glucose), is too high (hyperglycemia). Glucose is what the body uses for energy, and the pancreas produces a hormone called insulin that helps convert the glucose from the food you eat into energy. When the body does not produce enough insulin - or does not produce any at all - the glucose does not reach your cells to be used for energy.
There are two main types of Diabetes:
1. Type One Diabetes:
2. Type Two Diabetes:
**** Diabetes is a serious condition where your blood glucose level is too high. There are two main types, Type 1 and Type 2. They’re different conditions, but they’re both serious.
What is Type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes, which was formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is a chronic autoimmune condition that makes the body unable to produce insulin, which is the hormone that regulates blood sugar. Without insulin, our bodies cannot use the sugar in our bloodstream as energy, causing people to experience Diabetic ketoacidosis
How does Type 1 diabetes affect the body?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition, which means that the body’s immune system attacks itself. In the case of Type 1 diabetes, the body attacks the insulin-producing beta cells. These are the cells in the body that produce insulin. Over time, people with Type 1 diabetes are left with none of these beta cells, also known as islet cells, and therefore cannot produce their own insulin. Insulin is the hormone that allows the body to use the glucose (sugar) in the bloodstream as energy – it’s kind of acts as a key that unlocks the body’s cells, allowing glucose to enter and be absorbed. Converting blood glucose is the body’s main way that it gets energy, so without insulin, it must resort to breaking down bodily tissue such as muscle and fat stores. Another, potentially fatal, consequence for people with Type 1 diabetes who aren’t on insulin therapy is Diabetic Ketoacidosis.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
The most common form of diabetes is called type 2, or non-insulin dependent diabetes. This is also called “adult-onset” diabetes since it typically develops after age 35. However, a growing number of younger people are now developing type 2 diabetes. People with type 2 can produce some of their own insulin. Often, it’s not enough. And sometimes, the insulin will try to serve as the “key” to open the
How does type 2 diabetes affect body systems:
Type 2 diabetes is increasingly seen as a disease in which multiple organs and tissues in the body play a role in causing high blood glucose.
Muscle tissue:
Muscle tissue throughout the body contributes to elevated blood glucose by becoming resistant to insulin and unable to take up glucose for cellular energy needs.
Liver:
In type 2 diabetes, the liver—a major site of glucose storage—attempts to compensate for the decreased ability of the body to use glucose and increases glucose production.
Pancreas (beta and alpha cells):
Both alpha cells and beta cells in the pancreas play a central role in type 2 diabetes. Beta cells lose the ability to produce insulin, while alpha cells increase production of glucagon, the hormone that plays a role in transforming glycogen stored in the liver and muscles back into glucose. Additionally, beta cells also produce the hormone amylin, which controls how quickly glucose is released into the bloodstream after eating.
What problem can diabetes?
Diabetes is at risk for long-term problems affecting the eyes, kidneys, heart, brain, feet, and nerves. The best way to prevent or delay these problems is to control your blood sugar and take good care of yourself.
Eyes damage:
It is recommended that people with diabetes see an eye doctor every year for a dilated eye exam. Eye problems that can occur with diabetes include:
Cataracts: A clouding of the lens of the eyes
Glaucoma: Increased pressure in the eye
Retinopathy:
Eye changes with the retina in the back of the eye
Symptoms of eye problems include Blurred vision, Spots or lines in your vision, Watery eyes, Eye discomfort, Loss of vision. If you have any changes in your vision, call your healthcare provider.
Kidneys damage:
Protein in the urine is a sign of kidney disease. High blood pressure might also lead to kidney disease. Your blood pressure should be checked when you see your healthcare provider. Symptoms of a kidney problem include swelling of the hands, feet, and face, Weight gain from edema, Itching and/or drowsiness. (This can occur with end-stage kidney disease.) Prompt treatment may slow the changes with kidney disease. Heart and brain
All people with diabetes have an increased chance of heart disease and strokes. Heart disease is the major cause of death in people with diabetes. It is important to control other risks such as high blood pressure and high fats (cholesterol), as well as blood sugar.
Skin damage:
People with diabetes are more susceptible to a variety of skin problems, from dry skin to fungal infections. Mild skin problems may include dry skin, skin tacks, dark patches of skin. People with diabetes are also more likely to suffer from common skin problems, including bacterial infections like sties or boils, fungal infections like athlete's foot itching Roundish, brown, scaly patches develop in the harmless skin condition known as diabetic dermopathy.
Feet:
High blood sugars can lead to poor blood flow and nerve damage. This can lead to slow healing of sores. You can experience severe pain, but you can also lose feeling in your feet. In serious cases, this may lead to amputation of your toes, foot, or leg.
Symptoms of Heart Problem:
Shortness of breath, feeling faint, Feeling dizzy, Sweating, Nausea, Chest pain or pressure, Pain in the shoulders, jaw, and left the arm
Warning signs of a stroke: Sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, usually on one side of the body. Sudden nausea, Fever, Vomiting, Difficulty speaking or understanding words or simple sentences, Sudden blurred vision or decreased vision in one or both eyes, Difficulty swallowing, Dizziness, Loss of balance or loss of coordination, Brief loss of consciousness, Sudden inability to move part of the body (paralysis), Sudden intense headache, Call your doctor or go to an emergency room if any of these signs or symptoms occur.
Nerves: High blood sugars can affect all the nerve endings in your body. Nerve damage can cause many problems. Symptoms of nerve damage include Burning pain, Numbness, Tingling or loss of feeling in the feet or lower legs, Constipation, and diarrhea, Problems with sexual function in both men and women body’s cells, to allow the glucose to enter. But the key won’t work. The cells won’t open. This is called insulin resistance.
Diabetes and low blood sugar:
Diabetes affects your body’s ability to use insulin. Think of insulin as the key that unlocks your cells, letting glucose in for energy. People with diabetes use a variety of treatments to help their bodies use glucose in their blood. Among these are oral medications that increase insulin production and insulin injections. If you take too much of these types of medications, your blood sugar may drop too low. People also sometimes experience low blood sugar when planning to eat a big meal, but then they do not eat enough. Skipping meals, eating less than normal, or eating later than normal but taking your medication at your normal time can also lead to low blood sugar levels. Unplanned excess physical activity without eating enough can also cause a drop in blood sugar levels.
Cure of Diabetes & Control Yourself:
You can control Diabetes Yourself. if you eat healthier foods and vegetables more fiber, blood sugar drops. And exercise can increase the insulin sensitivity of muscles, which will then absorb more blood sugar. If diet and exercise alone won't do it, there are drugs that boost the muscle's sensitivity to insulin and curb blood sugar.
Previously came drugs on the market that control blood sugar in new and innovative ways. Blood-sugar testing has made huge strides too some monitors now require only tiny amounts of blood and give results in seconds. So much of this illness is under the patient's control. But having that much control over disease isn't a cakewalk. You may need to battle psychological demons to remain motivated over the long haul and learn how to live with diabetes and still feel alive. Good things, if you believe yourself, you can control 99% diabetes.
Diabetes Control of Foods:
The main principles of a diabetes diet are to consume plenty of whole grains, vegetables and fruits and to limit both fat and calories. High-fiber foods, fish and unsaturated fats are recommended, while saturated fats, sodium, cholesterol,and trans fats should be avoided as much as possible, Meals should be planned to keep you from experiencing spikes in blood sugar, as this can bring your blood sugar levels too high. Counting carbs, using the glycemic index or using diabetes exchange lists can make it easier to keep your blood sugar even throughout the day.
*** Note: AppleKhanFitnes Philosophy method is Diabetes patient needs the right foods and exercise. You may need steam/boiled vegetables, chicken, Fish, white eggs, fat-free milk, Peanuts, Brown Rice, Whole Wheat Bread, and Fruits. So, You can make your own menu Breakfast, Lunch and Dinner. You can see the Result within 7 days. It is very simple and you do not have to waste your time and money. So, make your life easy and enjoyable.
Cinnamon:
cinnamon has good sources of antioxidants. Antioxidants are important because they help the body reduce oxidative stress, a type of damage to cells, which is caused by free radicals. it is loaded with antioxidants that decrease oxidative stress. This may potentially protect against diabetes. In those with diabetes, either the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin or cells do not respond to insulin properly, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Cinnamon has the ability to lower blood sugar levels and improve your sensitivity to insulin. The consumption of cinnamon is associated with a statistically significant decrease in plasma glucose levels, LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Cinnamon consumption also helped increase HDL cholesterol levels.
Greek Yogurt and Oats:
Plain, low-fat Greek yogurt, or fat-free Greek yogurt, high in protein and calcium and relatively low in carbs and saturated fat, is the perfect breakfast when combined with whole-grain oats, yogurt, milk, and fruit, for a high-protein, high-fiber meal that will keep blood sugar and hunger in check.
Low-fat yogurt naturally contains both high-quality carbohydrates and protein, making it an excellent food for slowing or preventing an unhealthy rise in blood sugar. Diet high in calcium from yogurt and other calcium-rich foods is associated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes. Be sure to stick to low-fat or nonfat brands; fat-free Greek yogurt is my top pick because it has twice as much protein as regular nonfat yogurt.
Why do you eat yogurt?
Yogurt has a lot going for it. It’s rich in a number of nutrients, including
• Calcium • Protein • Potassium • Magnesium • Vitamin D • Vitamin B-12 • Vitamin B-2
Protein and magnesium are two key nutrients for diabetes management. Protein provides a feeling of fullness and can even out blood sugar levels. Magnesium helps improve insulin sensitivity, which can also help improve blood sugar levels.
Note: All fruits need to eat during the day.
Blueberries:
Blueberries are a rich source of polyphenols, which include anthocyanin bioactive compounds. Blueberries may help your body process glucose for energy efficiently, both increasing its sensitivity to insulin and managing blood sugar, which can help you fight diabetes. Epidemiological evidence indicates that incorporating blueberries into the diet may lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance was assessed by homeostatic model assessment-estimated insulin resistance.
Blueberries may help your body process glucose for energy efficiently, both increasing its sensitivity to insulin and managing blood sugar, which can help you fight diabetes.
Orange:
Oranges are full of fiber. Fiber takes longest to break down and digest. This enables slow release of sugar into the blood stream, which would further ensure that your blood glucose levels are stable for a long period of time.
Pears:
Pears contain good amounts of vitamins and minerals your body needs to stay healthy and fit. Pears are rich fiber in calcium, fol-ate, iron, potassium, magnesium, and vitamins C, E and K. Therefore, Pears control diabetic lower sugar level.
Green Apples:
Green Apples are good for diabetes patient because it has vitamin c & fiver. Fiber may also help improve fullness and cause weight loss while lowering blood sugar levels and boosting digestive function. The antioxidant effect of flavonoids in apples may protect cells from damage in the pancreas, an organ responsible for secreting insulin in response to extra sugar in the blood.
Kiwi:
Kiwi Rich in vitamin C, kiwi increases the body’s disease fighting abilities and immunity which are a food for diabetics. Containing vitamin E, kiwi is also rich in antioxidants and hence forms a great diet plan for diabetes.
Avocados:
Avocados are a great source of vitamins C, E, K, and B-6, as well as riboflavin, niacin, folate,
pantothenic acid, magnesium, and potassium. They also provide lutein, beta-carotene, and
omega-3 fatty acids. The good fats in avocado can help you prevent diabetes complications,
like heart attack and stroke, and help you use your insulin more effectively
Grapefruits:
Grapefruits has vitamin C, A powerful, water-soluble antioxidant that is present in high amounts
in grapefruit. It may protect cells from damage that often leads to heart disease and control diabetics.
Green vegetables:
Green leafy vegetables contain antioxidants, magnesium and omega 3 fatty acids — all of which have been shown to have health benefits. Leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables, and other green vegetables – are the most important foods to focus on for diabetes prevention and reversal. Higher green vegetable consumption is associated with lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Spinach:
Spinach is a rich source of fiber in vitamins, minerals and phytochemicals. Spinach possesses a low glycemic index, which means eating it will help support healthy and stable blood glucose levels. You Could include Spinach in your daily diet plan. You may consume spinach by making its delicious vegetables, soups and drink juice.
Green been:
Green beans contain considerable amounts of folate (vitamin B9) and other B-vitamins.
Folate is well-known for its importance in fetal development and the production of red blood cells. You can add this green bean your delicious meal daily base.
Asparagus:
Asparagus is a good source of antioxidants, including vitamins C and E, flavonoids and polyphenols. Antioxidants prevent the accumulation of harmful free radicals and may reduce your risk of chronic disease. It can keep diabetes by helping blood sugar levels stay
under control. You may include asparagus daily meal plan.
Cabbage:
Cabbage has a lot of antioxidant and antihyperglycemic properties that make it a medicine for diabetes. Cabbage is low in calls and carbs, high in fiber, low GI and GL. Plus, it has the potential to help lower blood sugar levels and aid in weight loss. You may add your daily meal plan.
Bitter melon:
Bitter Melon vitamins C, A, E, B-1, B-2, B-3, and B-9minerals like potassium, calcium, zinc, magnesium, phosphorus, and iron antioxidants like phenols, flavonoids. Bitter melon is linked to lowering the body's blood sugar. This is because the bitter melon has properties that act like insulin, which helps bring glucose into the cells for energy. You can add your daily meal plan.
Okra:
Okra is an excellent source of vitamins C and K1.Vitamin C is a water-soluble nutrient that contributes to your overall immune function, while vitamin K1 is a fat-soluble vitamin that’s known for its role in blood clotting and help decrease blood sugar levels.
Kale leaf:
The fiber and antioxidants in kale may offer protection against diabetes. Studies have shown that a high intake of fiber may lower blood glucose levels in people with type-1 diabetes. Those with type-2 diabetes may see improved blood sugar, lipids, and insulin levels. You can include daily meal plan kale vegetables and drink kale juice. You can make delicious soups, white eggs omelet’s, salad and drink juice.
Great Exercises For People With Diabetes:
1. Apple Control Diabetes Exercise:
Apple Control Diabetes Exercise movements are slow deep breath and mindful, gently stretching all of your joints and muscles in a single session. As you go from one movement to another, your body weight shifts from leg to leg.
Type 2 diabetes is a form of diabetes that usually sets in later in life. It is associated with chronic inflammation caused by increased glucose levels in the blood, known as hyperglycemia. When there is excess blood sugar, it can combine with hemoglobin, the oxygen transporter in the red blood cell, it can become glycated hemoglobin. This can be used to indicate the levels of excess sugars.
According to these responses, it is possible that Apple Control Diabetes Exercise can prompt a declination in blood glucose levels, perhaps by improving blood glucose metabolism, prompting a decrease in the inflammatory response. The exercise may boost levels of fitness along with a feeling of well being -- this, in turn, may boost the health of the immune system.
Apple Energy Exercise:
Apple Energy exercise is a unique movement, style, and Art. Apple energy movements are slow and mindful, which gently stretch the joints and muscles of the entire body, Applekhanfitness philosophy discovered how to boost energy your body with energy exercise. This exercise is creating your body power. If you do popper way deep breath in and breath out. You can keep additional energy for up to 8 hours. It's designed inside of human body.
Apple Energy exercise is breathing for all organs in the body. With the movement of the diaphragm, organs like the stomach, liver, intestine, heart, and pancreas are massaged, improving their function
Muscles have large stores of carbohydrate, called glycogen, which can be used to make ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate )from glucose. The body starts to supply working muscles with oxygen. So, we can have many benefits from Apple energy exercise.
Who can Learn & practice:
Apple energy exercise is a gentle art and slow movement. So much so that people of almost any age or physical condition can undertake it.
Reduce and Manage Your Stress Levels:
As you go through the movements, you pay close attention to your breath, using your nose to inhale and your mouth to exhale. Focus on taking a long, continuous breath without pausing between your inhale and exhale. This helps your body take in more oxygen, which boosts energy. It also forces you to concentrate on your breath, which encourages mindfulness. So, it’s really important you find ways to manage your stress levels daily.
Check your blood sugar as soon as you finish exercising and again several times during the next few hours. Exercise draws on reserve sugar stored in your muscles and liver. As your body rebuilds these stores, it takes sugar from your blood. The more strenuous your workout, the longer your blood sugar will be affected. Low blood sugar is possible even four to eight hours after exercise. Having a snack with slower-acting carbohydrates, such as a granola bar or trail mix, after your workout can help prevent a drop in your blood sugar.
1.Forward Bend Stretching the Back:
Sit with the legs straight. The hands rest on the thighs. Inhaling keep the arms straight and raise them above the head. Exhaling, keep the back straight, bend forward from the hips as far as possible and hold the toes. Keep straight Knees. Try to bring the head forward to touch the knees. Breathing normally hold this position. Inhaling bring the body upright keeping the arms straight. Exhaling place the hands on the thighs.
Benefits:
Increases blood supply in the back. Stretches the muscles of the back and along the back of the legs. Activates kidney and pancreas function and aids in achieving a slim figure.
2. Cobra Pose:
How to practice Cobra Pose?:
Step 1: Lie prone on the floor. Stretch your legs back, tops of the feet on the floor. Spread your hands on the floor under your shoulders. Hug the elbows back into your body
Step 2: Press the tops of the feet and thighs and the pubis firmly into the floor.
Step 3: On an inhalation, begin to straighten the arms to lift the chest off the floor, going only to the height at which you can maintain a connection through your pubis to your legs. Press the tailbone toward the pubis and lift the pubis toward the navel.
Step 4: the shoulder blades against the back, puffing the side ribs forward. Lift through the top of the sternum but avoid pushing the front ribs forward, which only hardens the lower back.
Step 5: Hold the pose anywhere from 15 to 30 seconds, breathing easily. Release back to the floor with an exhalation.
Benefits of Cobra Pose:
Stretches muscles in the shoulders, chest, and abdominal, Decreases stiffness of the lower back, Strengthens the arms and shoulders. Increases flexibility, Improves menstrual irregularities, Elevates mood. Stimulates organs in the abdomen, like the kidneys Relieve stress and fatigue. Opens the chest and helps to clear the passages of the heart and lungs. Improves circulation of blood and oxygen, especially throughout the spinal and pelvic regions, Strengthens the spine,
3 Twisting Pose:
How To Practice Twisting Pose?:
Sit on the floor& Fold your right leg and place it on the floor in such a way that your foot rests on the floor. Lift up your left hand and rest it against your right leg and twist your body towards the right-hand side. Rest your other hand on the floor. Remain steady in this twisted position for 30 seconds and then release. Repeat on the other side as well.
Benefits of Twisting Pose:
This Twisting pose gives a good stretch to your body, spine, legs, and hands. It keeps you away from minor backache problems. It keeps you away from neck problems as well. It increases your lungs’ capacity and improves your digestive system as well.
After exercise: Check your blood sugar again:
Note: Diabetes cure must be Right Nutrition & Right exercise.